Do you want to know How Do Convection Heaters Work? Let me tell you that a convection heater, also known as a convector heater, is a type of heating appliance that utilizes convection currents to heat and circulate air. In this article, I will delve into how this type of heater works and the different types available in the market.
These Convection heaters use convection currents to circulate warm air throughout a room. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at how these heaters work and why they might be a good choice for your heating needs.
How Do Convection Heaters Work?
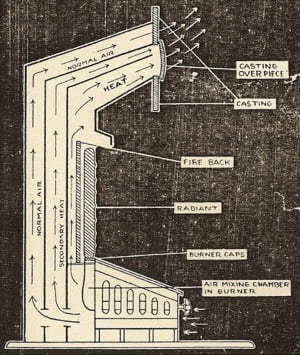
Convection heaters work on the principle of thermal conduction. The heating element in the heater warms up the air in the vicinity, which reduces its density relative to colder air, making it rise. As the heated air molecules rise, they displace cooler air molecules down towards the heating appliance. The displaced cool air is heated as a result, decreases in density, rises, and the cycle repeats itself.
What is the History of Convection Heating?
Convection heating dates back to ancient heating systems, including hearths, furnaces, and stoves, that operated primarily through convection. The development of convection heating technology has come a long way, with the publication of the first manual on fireplace design, Mechanique du Feu, in 1713, the creation of stoves with thermostatic control in 1849, and the rise of numerous cast iron stove manufacturers during the American Civil War.
What are the Types of Convection Heaters?
There are the several types of convection heaters available in the market, you can go through it.
1. Electric Convection Heaters:
Electric convection heaters use electricity to power their heating elements. These heaters are efficient and can be used in homes, offices, and small commercial settings. They are available in various sizes and types, including panel heaters and fan heaters.
2. Combustion or gas-fired heaters:
Combustion or gas-fired heaters use gas, propane, or any other type of fuel. These heaters are powerful and effective in large spaces but require proper ventilation due to the fumes they produce.
3. Panel Heaters:
Panel heaters are a type of electric convection heater commonly used for heating rooms in residential and small commercial settings. They are often mistaken for electric radiators, which are devices that use radiant heating and transfer heat directly to objects rather than using the air as a medium.
4. Fan Heaters:
Fan heaters combine the warming capability of a heater and air distribution capacity of a fan. Modern fan heaters have variable-speed fans that can work independently from the heating element.
5. Institutional Convector Heater:
Institutional convector heaters are heavy-duty heaters designed strictly for commercial and industrial use. They are built with a broad surface area and can withstand harsh environments.
6. Oil Heaters:
Oil heaters, also called column heaters, are electrically heated and use oil as a heat reservoir. Because oil has a high heat capacity and boiling point, it is a suitable heat pathway between the heating element and the cavities of the heater unit.
Conclusion:
Convection heaters offer a cost-effective and efficient way to heat your home or office. When choosing a convection heater, it is important to consider factors such as the size of the space you need to heat, the type of heater, and its power source. With the various types available, you can find the perfect fit for your needs.




0 Comments